Explore pneumonia and its connection to the RSV virus, along with vaccine effectiveness and preventive measures to safeguard your health.As the seasons change and respiratory illnesses become more prevalent, understanding the relationship between pneumonia, RSV (respiratory syncytial virus), and vaccinations is crucial. Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and RSV is a common viral infection known to cause severe respiratory distress, particularly in infants and older adults. This blog post aims to explore the connection between these two respiratory threats, delve into the effectiveness of the pneumonia vaccine, and highlight preventative measures that can help protect vulnerable populations. With growing concerns about respiratory infections, particularly in high-risk groups, it’s important to uncover whether the pneumonia vaccine offers any shield against RSV and how we can best guard against these conditions. Join us as we navigate this essential health topic and offer insights on staying safe during respiratory season.
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus. This condition can be caused by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening, particularly in vulnerable populations like the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions.
The symptoms of pneumonia often include a persistent cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. While some might experience a cold or flu-like illness, others may feel much sicker, with decreased oxygen levels leading to complications. As a result, it’s critical to seek medical attention if pneumonia is suspected.
Diagnosing pneumonia typically involves a physical examination, the review of medical history, and various tests such as x-rays or blood tests. Treatment usually depends on the type and severity of the infection, which may include antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia or antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
Understanding the RSV virus
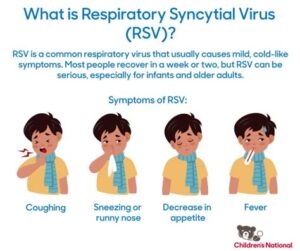
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that primarily causes respiratory infections in infants and young children. It can lead to severe respiratory issues and is known for its high prevalence during the winter months. Understanding RSV is crucial as it affects a vast number of children every year.
RSV is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Additionally, it can survive on surfaces for several hours, making it easy to contract through contact with contaminated objects. The symptoms of RSV typically include a runny nose, coughing, sneezing, and in some cases, it can progress to bronchiolitis or pneumonia.
There’s a significant link between RSV and more severe respiratory conditions, particularly in infants who are premature, have heart issues, or compromised immune systems. While most children will recover from RSV in a week or two, some may require hospitalization, highlighting the importance of vaccination and preventive measures.
The link between pneumonia and RSV
Respiratory Syncytial Virus, commonly known as RSV, is a significant cause of respiratory infections in infants and young children. It is crucial to understand how it relates to pneumonia, a serious complication that can arise from RSV infections. When a child or adult contracts RSV, the virus infects the airways and can lead to inflammation, which may eventually trigger pneumonia.
Studies have shown that individuals infected with RSV are at an increased risk for developing pneumonia. This can occur especially in vulnerable populations, such as premature infants, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. The link between RSV and pneumonia is particularly concerning, as pneumonia resulting from RSV can lead to severe health complications and even hospitalization.
| Population | Risk of Pneumonia from RSV |
|---|---|
| Infants under 6 months | Higher risk of hospitalization |
| Elderly individuals | Increased likelihood of complications |
| Individuals with respiratory issues | More susceptible to severe pneumonia |
Understanding the link between pneumonia and RSV is essential for implementing appropriate health measures. Early detection and treatment of RSV infections can help mitigate the risk of pneumonia, protecting those most at risk.
Effectiveness of the pneumonia vaccine
The pneumonia vaccine is designed to offer protection against various strains of the bacteria that can cause pneumonia, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae. This vaccine plays a crucial role in reducing the incidence of pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
Research has shown that the pneumonia vaccine is effective in decreasing the risk of severe pneumonia cases that may lead to hospitalization. It is important to note that while the vaccine targets specific bacterial strains, it does not provide protection against all pneumonia-causing pathogens, including viruses such as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).
To illustrate the effectiveness, studies demonstrate that vaccination can reduce the risk of pneumonia hospitalization by up to 50% in certain populations.
| Prevention Method | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Pneumonia Vaccine | Reduces risk by up to 50% |
| Hand Hygiene | Variable, highly effective in reducing infections |
| Healthy Lifestyle Factors | Contributes to overall health, indirect impact on pneumonia risk |
Preventative measures for RSV
Respiratory Syncytial Virus, commonly known as RSV, is a significant cause of respiratory illness in infants and young children. Preventing the spread of RSV is crucial for safeguarding vulnerable populations.
| Preventative Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Regularly washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds can significantly reduce the transmission of RSV. |
| Avoiding Close Contact | Minimize close interaction with sick individuals, especially during RSV season. |
| Cleaning Surfaces | Frequent sanitization of commonly touched surfaces, such as doorknobs and toys, helps in curbing the spread of the virus. |
| Breastfeeding | Breastfeeding provides antibodies that can strengthen an infant’s immune system, potentially reducing the severity of RSV infections. |
| Limiting Exposure | Keeping infants away from crowded places during peak RSV season is advisable to reduce their risk of infection. |
RSV spreads mainly through respiratory droplets, making it vital to implement these measures, especially in childcare settings or households with at-risk children. Remember, early identification and prevention can greatly minimize the impact of RSV outbreaks.
By taking proactive steps, families can create a safer environment for infants and young children, ensuring fewer cases of serious illness caused by RSV. Awareness and education about the virus and its transmission dynamics are essential components in combatting its spread.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing preventative measures can drastically reduce the incidence of RSV infections. These measures not only protect individual children but also contribute to the overall health of the community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RSV and how does it relate to pneumonia?
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that causes respiratory infections, particularly in young children. While RSV can lead to pneumonia, the pneumonia vaccine specifically targets bacterial pneumonia, not viral infections like RSV.
Does the pneumonia vaccine offer any protection against RSV?
No, the pneumonia vaccine does not provide protection against RSV, as it is designed to protect against bacterial strains such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Who should receive the pneumonia vaccine?
The pneumonia vaccine is recommended for young children, the elderly, and individuals with certain health conditions that make them more susceptible to pneumonia.
Can RSV lead to pneumonia in vulnerable populations?
Yes, RSV can cause pneumonia, particularly in infants, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems.
What are the symptoms of RSV infection?
Common symptoms of RSV include coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, fever, and runny nose. In some cases, it can lead to more severe respiratory illness.
Are there any vaccines specifically for RSV?
As of now, there are no widely available vaccines specifically for RSV, but research is ongoing, and promising candidates are being developed.
How can RSV infections be prevented?
Preventative measures against RSV include practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and ensuring that high-risk infants receive palivizumab, a prophylactic treatment.