Explore the RSV vaccine’s understanding, activation time, influencing factors, clinical trials, and effectiveness to gain insights into its impact on respiratory illnesses.As respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) continues to pose a significant health threat, especially to infants and the elderly, understanding the nuances of the RSV vaccine becomes increasingly important. One pressing question that many individuals have is how long it takes for the RSV vaccine to become effective after administration. In this blog post, we will explore what the RSV vaccine entails, the activation timeline post-vaccination, and various factors that can influence its effectiveness. Additionally, we will delve into the clinical trials that have shaped our understanding of the vaccine and discuss how we measure its efficacy in real-world scenarios. Join us as we unpack these crucial elements to better inform you about this vital tool in combating RSV.
Understanding RSV Vaccine
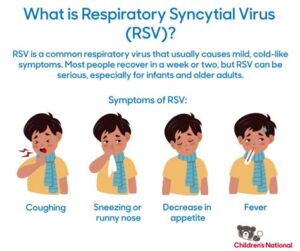
The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. For many, it behaves like a typical cold, but for infants, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems, it can lead to severe respiratory diseases. To combat this, researchers have developed the RSV vaccine, which is designed to provide protection against this potentially dangerous virus.
The RSV vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight the virus more effectively. There are different types of vaccines, including live attenuated and inactivated vaccines, with ongoing research focused on improving their efficacy. Each vaccine variant can influence its effectiveness and the time it takes for the body to build immunity.
Once administered, the RSV vaccine typically requires a certain duration to reach optimal effectiveness. This period can vary based on several factors, including the person’s age, health status, and the specific vaccine formulation used. Some studies show that immunity can start developing within a few days to weeks, but it may take longer for full protection to manifest.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of the RSV vaccine, including its mechanisms and the time it takes for immunity to build up, is crucial for individuals at risk and for publ
Activation Time of RSV Vaccine
The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) vaccine is a significant advancement in our efforts to combat respiratory illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations such as infants and the elderly. One of the most critical aspects of vaccine implementation is understanding the activation time—the duration it takes for the body to build immunity after vaccination.
Typically, the activation time for the RSV vaccine can range from a few days to several weeks. After vaccination, the immune system begins to recognize the virus and mounts a response. It’s essential to consider several factors that can influence this timeline, including the individual’s age, health status, and the specific type of RSV vaccine administered.
| Type of RSV Vaccine | Average Activation Time |
|---|---|
| Live Attenuated Vaccine | 1-2 weeks |
| Subunit Vaccine | 2-4 weeks |
| mRNA Vaccine | 1-3 weeks |
Overall, it’s crucial to allow adequate time for the RSV vaccine to fully activate and provide protection. Healthcare professionals usually recommend that individuals receive their vaccination well in advance of the RSV season to ensure optimal immunity. Hence, understanding the activation time is vital for effective health planning and management of RSV infections.
Factors Affecting Vaccine Time
When it comes to the RSV vaccine, understanding the various factors that influence its activation time is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. Several elements can affect how quickly the vaccine becomes effective in promoting an immune response.
One of the primary factors is the age of the individual receiving the vaccine. Infants and young children may respond differently to immunization compared to adults due to their developing immune systems. Additionally, those with compromised immune systems or existing health conditions may experience a delayed response.
Another significant factor is the strain of the RSV virus present in the population. Different strains may elicit varying levels of immune response, and the vaccine must be aligned with the circulating strains to ensure effectiveness. Moreover, the timing of vaccination can also play a role — for instance, receiving the vaccine during peak RSV season may lead to a quicker immunological response compared to off-season vaccinations.
Additionally, the formulation and storage conditions of the vaccine are important. If not stored at the correct temperature, the vaccine’s effectiveness can be compromised, leading to delays in reaching full immunity. Understanding these factors can help guide vaccination strategies and improve outcomes for those at risk of RSV.
Clinical Trials of RSV Vaccine
The development of the RSV vaccine has been a significant focus of research, as the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a leading cause of severe respiratory illness in infants and young children. Clinical trials are essential for understanding the safety and effectiveness of these vaccines. During these trials, researchers assess various doses of the vaccine to determine how well it works and identify any potential side effects.
- Phase 1: Focuses on safety and finding the right dose.
- Phase 2: Expands the group of participants to further evaluate safety and effectiveness.
- Phase 3: Involves a larger population to confirm findings and compare the vaccine to a placebo.
It’s crucial for participants in these trials to meet certain criteria. For example, many trials target specific age groups, such as infants under two years old, who are most susceptible to the effects of RSV. Various factors, such as immunocompromised states or pre-existing conditions, are considered when selecting participants. These rigorous testing protocols ensure that any RSV vaccine that reaches the market has u
Measuring Effectiveness of RSV Vaccine
Measuring the effectiveness of the RSV vaccine is crucial for understanding its impact on public health and for guiding future vaccination strategies. The effectiveness of a vaccine refers to how well it performs in real-world conditions, particularly in preventing disease among the vaccinated population. This measurement is typically established through various study designs, including clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the RSV vaccine, researchers rely on multiple factors, such as the rate of severe RSV infections among vaccinated individuals compared to those who are unvaccinated.
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccine Efficacy | Comparison of disease incidence between vaccinated and unvaccinated groups |
| Immunogenicity | Assessment of the immune response generated by the vaccine |
| Seroprevalence | Percentage of the population with protective antibody levels |
The results of these assessments provide vital information on whether the RSV vaccine can significantly reduce the burden of disease in the population. Various studies have reported favorable outcomes, showing that vaccinated individuals exhibit a reduced incidence of RSV-related hospitalizations, particularly among high-risk populations such as infants and the elderly. Ongoing studies continue to gather data to ensure that the v
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the RSV vaccine?
The RSV vaccine is designed to protect against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), a common virus that can lead to severe respiratory infections, especially in young children and the elderly.
How long does it take for the RSV vaccine to become effective?
The RSV vaccine typically takes about 1 to 2 weeks after administration to build sufficient immunity in the body.
What factors can influence the effectiveness of the RSV vaccine?
Factors such as age, health status, and the presence of underlying medical conditions can influence how effectively the vaccine works in an individual.
Are there any side effects from the RSV vaccine?
Common side effects of the RSV vaccine may include soreness at the injection site, mild fever, or fatigue, but serious side effects are rare.
Who should get the RSV vaccine?
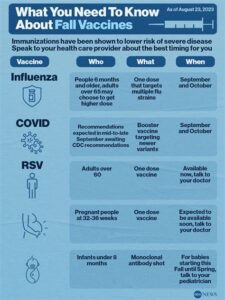
The RSV vaccine is recommended for infants, young children, and older adults, particularly those at higher risk for severe RSV illness.
Can you still get RSV after being vaccinated?
While the RSV vaccine significantly reduces the risk of severe illness, it does not guarantee complete prevention, and breakthrough infections can still occur.
When is the best time to get the RSV vaccine?
The best time to receive the RSV vaccine is typically before the RSV season begins, which usually occurs in the fall and winter months.