Explore the RSV vaccine’s benefits, recommended frequency, effects on at-risk groups, safety concerns, and future research developments in this informative guide.As respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) continues to pose a significant health risk, particularly for vulnerable populations, understanding the RSV vaccine’s role is essential. The introduction of this vaccine has sparked numerous questions about its effectiveness and the recommended frequency of administration. In this blog post, we will delve into what the RSV vaccine is, highlighting its importance in protecting individuals, especially the at-risk groups. We’ll explore current frequency recommendations, the impacts on vulnerable populations, discuss potential side effects and safety concerns, and look at future developments and research surrounding this critical vaccine. Whether you’re considering the vaccine for yourself or a loved one, gaining clarity on these aspects will help empower informed decisions in the fight against RSV.
What is the RSV vaccine?
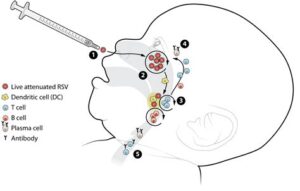
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that causes respiratory infections, particularly in infants and young children. The RSV vaccine is designed to help protect against severe cases of RSV, which can lead to bronchiolitis and pneumonia. This vaccine is particularly crucial for at-risk populations, such as premature infants and those with underlying health conditions.
Several types of RSV vaccines are being developed, each targeting different responses from the immune system. The primary goal of these vaccines is to reduce the severity of the infection and subsequently lower hospitalizations related to RSV. Researchers have made significant advancements, leading us closer to vaccines that can provide long-term immunity and are safe for use in infants.
The urgency for an effective RSV vaccine comes from the virus’s high prevalence and the significant healthcare burden it imposes. By preventing severe infections, the vaccine not only protects vulnerable populations but also alleviates the strain on healthcare systems during peak RSV seasons.
Frequency recommendations
The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) vaccine is an important immunization aimed at reducing the incidence of severe respiratory illness caused by the virus. Understanding how often individuals should receive this vaccine is crucial, especially for those in at-risk populations. The frequency recommendations vary based on certain factors, such as age, underlying health conditions, and guidelines that may evolve with the healthcare landscape.
Currently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that certain groups receive the RSV vaccine under specific circumstances. For infants and young children at high risk, the vaccine is typically administered every month during the RSV season, which usually spans from fall to spring. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) also emphasizes the need for reevaluation of immunization strategies annually based on disease prevalence.
For older adults or individuals with chronic health conditions, the recommendations may vary. It is advised that these individuals consult with their healthcare providers to determine their specific needs regarding the RSV vaccine. Factors such as previous infections and immune response will guide the decision on frequency and boosters, underscoring the importance of personalized healthcare in managing RSV risk.
Impact on at-risk populations
The RSV vaccine is particularly significant for certain at-risk populations. These groups include infants, older adults, and individuals with underlying health conditions. Understanding the impact of the RSV vaccine on these communities is crucial for public health.
For infants, especially those born premature or with congenital heart or lung conditions, the RSV virus can lead to severe respiratory distress. The vaccine aims to provide protection during the RSV season, significantly reducing hospitalizations and severe complications. According to recent studies, infants who receive the vaccine show a marked decrease in RSV-related illnesses compared to those who do not.
Older adults, particularly those over 65, are also at increased risk of severe RSV disease. The vaccine can help minimize the risk of serious complications such as pneumonia, which can be life-threatening in this age group. With the growing elderly population, the importance of the RSV vaccine in protecting this demographic cannot be emphasized enough.
Additionally, individuals with chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions may experience more severe RSV outbreaks. By vaccinating these at-risk populations, we can significantly lower the disease burden and enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Side effects and safety concerns
The RSV vaccine has been a significant advancement in reducing the impact of respiratory syncytial virus, particularly among vulnerable populations such as infants and the elderly. However, like all vaccines, there are potential side effects and safety concerns that must be carefully considered.
Common side effects reported include mild symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and soreness at the injection site. These reactions are typically short-lived and resolve on their own. In rare cases, more severe reactions can occur, which may include allergic reactions or anaphylaxis. It’s essential for individuals and caregivers to be aware of these possibilities and seek medical attention if they observe unusual symptoms following vaccination.
Another aspect of safety concerns revolves around specific at-risk populations, such as those with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions. While the vaccine is generally considered safe, these individuals may experience different reactions or complications. Health care providers should evaluate each case individually, weighing the benefits of vaccination against potential risks.
In conclusion, while the RSV vaccine plays a critical role in preventing serious respiratory illnesses, ongoing monitoring and research into its safety and side effects are crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of all populations.
Future developments and research
The research surrounding the RSV vaccine is continuously evolving, with numerous studies aimed at enhancing its effectiveness and safety. Researchers are exploring various vaccine platforms, including live attenuated, subunit, and mRNA vaccines, to provide broader immunity. Insights gained from these studies could lead to the introduction of more robust vaccines that are effective against multiple strains of the virus.
One exciting area of investigation includes the development of vaccines for specific populations. Young children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). By tailoring future vaccine candidates to generate a more targeted immune response in these groups, the goal is to achieve higher levels of protection. Clinical trials are currently being conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of these tailored vaccines.
Moreover, researchers are delving into the potential for combination vaccines that could simultaneously target RSV along with other prevalent infections, such as influenza. This could simplify vaccination schedules and improve overall public health outcomes. As the landscape of vaccine technology progresses, future developments in RSV vaccines hold the promise of significantly reducing the burden of RSV-associated diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the RSV vaccine?
The RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) vaccine is designed to protect individuals, particularly infants and young children, from infections caused by the RSV, which can lead to severe respiratory illnesses.
Who should receive the RSV vaccine?
The RSV vaccine is generally recommended for infants, especially those at high risk, such as premature babies or those with underlying health conditions. Adults, especially those in close contact with high-risk infants, may also be advised to get vaccinated.
How often do you need the RSV vaccine?
The frequency of RSV vaccination can depend on individual risk factors. For infants at high risk, the vaccine may be administered monthly during RSV season, while recommendations for adults vary based on specific guidelines.
Are there any side effects of the RSV vaccine?
Common side effects of the RSV vaccine might include mild fever, irritability, and soreness at the injection site. Severe side effects are rare but can occur.
When is RSV season?
RSV season typically occurs in the fall and winter months, peaking between December and February in many regions, which is when vaccination and preventive measures become most critical.
Can adults benefit from the RSV vaccine?
Currently, RSV vaccines are primarily targeted toward infants and young children, but research is ongoing to develop effective vaccines for adults, particularly the elderly and those with weakened immune systems.
How effective is the RSV vaccine?
The effectiveness of the RSV vaccine can vary, but it has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of severe RSV infections in infants at high risk, providing important protection during peak RSV season.