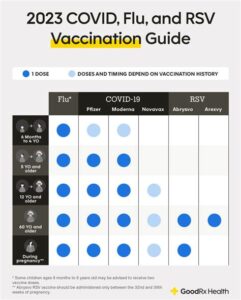
Discover essential insights on vaccine timing, including wait times, virus incubation periods, influencing factors, professional guidance, and maximizing effectiveness for your health.Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common yet potentially serious virus that affects the respiratory tract, especially in young children and the elderly. As the world grapples with seasonal outbreaks, many individuals wonder about the timing of vaccination following an RSV infection. How soon can you receive the vaccine after recovering from the virus? This blog post aims to shed light on this crucial question, addressing the recommended wait time for vaccination, the virus’s incubation period, and other factors that may influence your timing. We will also emphasize the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional to ensure you receive the optimal benefits from the vaccine. Understanding these aspects can help you stay informed and protected, enhancing your overall health and well-being in the face of RSV.
The recommended wait time
After recovering from RSV (respiratory syncytial virus), many individuals may wonder about the appropriate time frame for receiving vaccinations, particularly in relation to other respiratory illnesses. It is essential to acknowledge that the recommended wait time before getting vaccinated can vary based on individual circumstances.
Generally, health experts advise waiting at least two to four weeks after the symptoms of RSV have fully resolved. This allows the immune system sufficient time to recover and reduces the risk of any adverse reactions to the vaccine.
In special circumstances, such as individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. They can provide tailored recommendations and possibly adjust the wait time based on specific health factors.
Understanding the virus incubation period
When discussing respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and its implications for vaccination, it’s crucial to understand the concept of the incubation period. The incubation period for RSV typically ranges from 2 to 8 days, with most cases appearing around 4 to 6 days after exposure.
During the incubation period, the virus replicates in the respiratory tract, and an individual remains asymptomatic, meaning they do not display noticeable signs of illness. This period is significant because it affects both the timing of vaccine administration and the potential for onward transmission to others.
In the context of RSV, the incubation period is essential for determining when to receive the vaccine after an RSV infection. It’s recommended to wait until the virus has cleared from your system before getting vaccinated, ensuring
Factors affecting vaccine timing
When considering how soon after having RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) one can receive the vaccine, several key factors come into play. Understanding these factors can help individuals ensure they are making informed decisions regarding their health.
One primary factor is the individual’s immune status. Patients with a compromised immune system may need to wait longer before receiving the vaccine, as their bodies may not respond effectively to it. Additionally, the severity of the initial RSV infection can influence the timing. Those who experienced more severe symptoms should consult with healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate time for vaccination.
Other factors include age, underlying health conditions, and any recent treatments that the individual may have undergone. For infants and young children, pediatric guidelines often recommend specific waiting periods after an RSV diagnosis to ensure their safety and the effectiveness of the vaccine. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to evaluate these factors and establish the best timing for vaccination.
Consulting with a healthcare professional
When it comes to understanding the right timing for vaccination after recovering from RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), consulting with a healthcare professional is essential. This process allows for personalized guidance based on individual health circumstances, ensuring that one receives the most accurate recommendations for vaccination.
A healthcare provider can assess your unique health history and any underlying conditions that may influence the effectiveness of the vaccine. They can also evaluate any recent illness, shedding light on whether you should wait longer before getting vaccinated. This is crucial as the body’s immune response can be affected by recent infections.
During your consultation, be sure to discuss any questions or concerns you may have about the vaccine. It’s important to understand the benefits and risks associated with vaccination post-RSV. A well-informed decision will ultimately lead to better health outcomes and peace of mind.
Ensuring optimal vaccine effectiveness
When it comes to vaccines, particularly after an infection like RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), ensuring optimal vaccine effectiveness is crucial. It’s essential to understand that the timing of receiving a vaccine can significantly impact its efficacy, especially if you have recently recovered from an illness.
One of the primary factors influencing vaccine effectiveness is the body’s immune response. After recovering from RSV, your immune system may still be in a state of fluctuation. If you get vaccinated too soon after an infection, your body might not respond as robustly as it would if you waited a little longer. Hence, it’s vital to allow your immune system adequate time to stabilize before receiving the vaccine.
Moreover, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to determine the best timing for getting vaccinated post-RSV. They can assess your specific health situation, consider factors such as previous illnesses or current health conditions, and recommend an appropriate schedule. By doing this, you can maximize the effectiveness of the vaccine and help ensure you have the best protection going forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RSV?
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) is a common virus that causes respiratory infections, particularly in children and infants.
How is RSV transmitted?
RSV is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, as well as through direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
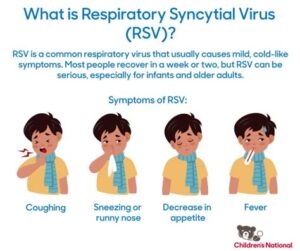
What are the symptoms of RSV?
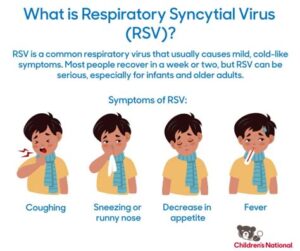
Symptoms of RSV may include coughing, sneezing, runny nose, fever, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
What vaccine is available for RSV?
Currently, there is no approved vaccine for RSV in the general population, though some vaccines are in development.
How long after recovering from RSV can you get vaccinated?
Generally, individuals can receive vaccines 4 to 6 weeks after recovering from RSV; however, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Are there any side effects of the RSV vaccine?
Since there is no widely available RSV vaccine yet, potential side effects are still being studied. For vaccines under development, common side effects may include pain at the injection site, fever, or fatigue.
Why is it important to consider vaccination after RSV?
Vaccination can help prevent severe cases of other respiratory illnesses that can be complicated by a previous RSV infection, improving overall health outcomes.