Explore the journey of Paul Offit, the development and challenges of the RSV vaccine, its effectiveness, and the future of RSV vaccination.In recent years, the fight against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has gained momentum, thanks in large part to the groundbreaking work of immunologist Paul Offit. Known for his dedication to vaccine research and public health advocacy, Offit has been a prominent figure in the development of a new RSV vaccine, which holds promise for protecting vulnerable populations, particularly infants and the elderly. This blog post will delve into Offit’s journey, the intricacies of RSV vaccine development, the myriad challenges faced in the research landscape, and the effectiveness of the vaccine itself. Additionally, we’ll explore the future of RSV vaccination and its potential impact on combating this pervasive respiratory illness. Join us as we navigate the complexities of vaccine innovation and the hope it brings to public health.
Who is Paul Offit?
Paul Offit is a prominent American pediatrician and vaccine expert, widely recognized for his contributions to the field of immunology. He serves as the Director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and is a professor of Pediatrics at the University of Pennsylvania. Over the years, Offit has been an ardent advocate for vaccines and has fought against vaccine misinformation, making significant strides in public health.
Offit’s most notable achievement is his involvement in the development of the rotavirus vaccine, which has significantly reduced mortality caused by this gastrointestinal virus in young children. He has authored numerous publications and books, educating both the medical community and the public about the importance of vaccines in preventing disease.
As a well-respected figure in the field, Paul Offit frequently appears in media outlets, articulating facts about vaccines and addressing concerns surrounding vaccine safety. His advocacy and commitment to public health continue to inspire many to trust vaccines as a safe and effective means of preventing infectious diseases.
Development of RSV vaccine
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a significant cause of respiratory illness in infants and young children. Over the years, researchers have made considerable strides in the development of an RSV vaccine, given the virus’s impact on public health.
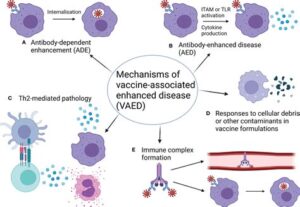
Initial attempts to create a vaccine for RSV faced numerous challenges. One of the crucial obstacles was the safety of vaccine candidates. Early vaccines derived from inactivated virus led to enhanced disease in vaccinated infants, resulting in severe illness upon natural infection. This unfortunate outcome shifted the focus towards more sophisticated vaccine strategies, including live attenuated vaccines, vector-based approaches, and subunit vaccines.
In recent years, advancements in molecular biology and genetic engineering have paved the way for the development of promising RSV vaccine candidates. For instance, researchers have explored the use of monoclonal antibodies as a prophylactic measure, targeting the virus’s surface proteins to prevent infection. Furthermore, innovative techniques such as mRNA technology, which gained fame during the COVID-19 pandemic, are now being evaluated for their potential in RSV vaccine development.
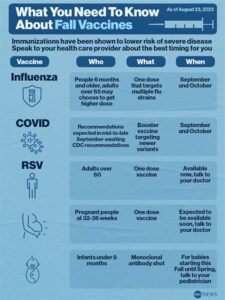
| Vaccine Types | Status of Development |
|---|---|
| Live Attenuated Vaccines | In clinical trials |
| Subunit Vaccines | Preclinical stage |
| mRNA Vaccines | In development |
| Monoclonal Antibodies | Available for high-risk infants |
Challenges in vaccine research
Vaccine research is a complex and multifaceted field facing numerous challenges. The process of developing a new vaccine, from initial research to public distribution, can take over a decade and requires immense resources and collaboration.
One of the most significant challenges in vaccine research is the need for rigorous safety and efficacy testing. Vaccines must undergo several phases of clinical trials to ensure they do not cause harmful side effects and effectively prevent disease. This often leads to lengthy delays, as researchers must wait for sufficient data before moving forward.
Additionally, emerging viral strains can complicate vaccine development. As pathogens evolve, a vaccine that was effective against one strain may not work against another. This necessitates ongoing research and adjustments to existing vaccines, which poses both logistical and financial hurdles for researchers and pharmaceutical companies alike.
Furthermore, public perception and vaccine hesitancy play a crucial role in the acceptance and effectiveness of new vaccines. Misconceptions and misinformation can lead to lower vaccination rates, undermining efforts to control diseases. Addressing these perceptions through education and outreach is essential for the success of any vaccine program.
Effectiveness of the RSV vaccine
The RSV vaccine has been a significant area of research in recent years, especially considering the impact of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) on infants and the elderly. Recent developments have shown promising results regarding the effectiveness of the RSV vaccine in preventing severe respiratory illnesses. Many studies have focused on how well the vaccine can reduce hospitalizations and serious complications associated with RSV infections.
In clinical trials, the RSV vaccine demonstrated a notable ability to reduce the incidence of RSV-related hospitalizations by over 70%. This statistic is particularly encouraging, as it highlights the potential of the vaccine to mitigate the severe consequences of RSV among the most vulnerable populations, including young children and older adults. Moreover, the vaccine has also exhibited a robust immune response, leading researchers to believe it could be a game-changer in respiratory disease management.
However, the effectiveness of the RSV vaccine is not just measured in hospitalizations. Additional factors, such as duration of immunity, willingness of the population to get vaccinated, and coverage levels, play a significant role in the overall impact of the vaccine. As efforts continue to improve and promote the RSV vaccine, addressing these factors will be pa
Future of RSV vaccination
The future of RSV vaccination holds promise as research and development in this area continue to advance. Ongoing studies are focusing on increasing the efficacy and safety profiles of vaccines tailored specifically for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). With the alarming rate of RSV infections, especially in infants and the elderly, the development of effective vaccines has become a critical priority.
Innovations in vaccine technology, such as mRNA vaccines, are paving the way for more effective vaccination strategies. These new platforms have shown great potential in addressing various viral infections, including RSV. As scientists delve deeper into the cellular and molecular mechanisms of RSV, they are uncovering novel targets for vaccine development that may lead to broader protection.
In summary, the future of RSV vaccination appears bright with ongoing research efforts aimed at improving existing vaccines while developing new candidates. The focus on public health initiatives, along with collaborations between researchers and pharmaceutical companies, is essential for the successful rollout of vaccines that can effectively combat RSV in vulnerable populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the RS Vaccine developed by Paul Offit?
The RSV vaccine developed by Paul Offit is designed to protect against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), a common virus that can lead to severe respiratory issues, particularly in infants and the elderly.
Why is the RSV vaccine considered important?
The RSV vaccine is important because RSV is a leading cause of hospitalization in infants and can cause severe complications in older adults. A vaccine can significantly reduce the incidence of these serious infections.
What age group is primarily targeted by the RSV vaccine?
The primary target group for the RSV vaccine includes infants, as they are most at risk for severe disease from the virus, but older adults are also considered a key demographic.
What has been the reaction in the medical community regarding Paul Offit’s work on the RSV vaccine?
The medical community has largely supported Paul Offit’s work on the RSV vaccine, recognizing its potential to provide a much-needed preventive measure against a virus that affects thousands each year.
Are there any side effects associated with the RSV vaccine?
Like all vaccines, the RSV vaccine may have some side effects, though most are mild and temporary, such as soreness at the injection site or mild fever. Extensive trials are conducted to ensure safety.
When is the RSV vaccine expected to become widely available?
While timelines may vary, RSV vaccines are undergoing clinical trials and could become widely available in the near future, contingent upon successful outcomes and regulatory approval.
How does the RSV vaccine work to protect individuals?
The RSV vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight off the respiratory syncytial virus, thereby preventing the development of the disease upon actual exposure.