Discover the workings and benefits of Prolia and the importance of the RSV vaccine in protecting health against serious infections.In recent years, the conversation around preventive healthcare has shifted significantly, particularly concerning osteoporosis and respiratory illnesses. One medication that has garnered attention is Prolia, primarily used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and individuals at high risk for fractures. Simultaneously, the RSV vaccine emerges as a crucial tool in safeguarding vulnerable populations against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which can lead to severe respiratory issues, especially in infants and the elderly. In this blog post, we’ll explore how Prolia works and its benefits in managing osteoporosis, while also delving into the importance of the RSV vaccine in protecting against respiratory infections. By understanding these two vital components of healthcare, we can better advocate for our health and well-being.
Understanding Prolia
Prolia (denosumab) is a medication primarily used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and to increase bone mass in men at high risk for fracture. It is also prescribed for patients undergoing hormone ablation therapy for cancer. Prolia works by inhibiting a protein called RANKL (Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Β Ligand), which plays a crucial role in the formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts—cells responsible for bone resorption.
By blocking RANKL, Prolia effectively reduces bone resorption, leading to an increase in bone density and a decrease in the likelihood of fractures. This is particularly beneficial for those who have low bone density or are at high risk due to conditions such as hormone-related cancers or age-related bone loss.
Patients using Prolia receive the medication via a subcutaneous injection every six months. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor bone health and ensure that the treatment is effective. It is important to discuss with your healthcare provider any potential side effects, including an increased risk of infections, skin reactions, or rare cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw.
How Prolia Works
Prolia, also known as denosumab, is a medication used primarily for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and for patients who are at high risk of bone fractures. Understanding how Prolia works is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Prolia operates by targeting the RANK/RANKL pathway, which plays a crucial role in the regulation of bone metabolism. Prolia inhibits the interaction between RANK ligand (RANKL) and its receptor, RANK, thereby reducing the formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts—cells that break down bone tissue.
The result of this inhibition is a decrease in bone resorption, leading to an increase in bone mineral density (BMD) and a reduction in the risk of fractures. Patients taking Prolia often experience improved bone health due to this mechanism of action.
In summary, the efficacy of Prolia as a treatment option stems from its unique ability to interrupt the bone resorption process, making it a valuable agent in osteoporosis management.
Benefits of Prolia
Prolia (denosumab) is a medication that offers numerous benefits, particularly for individuals with osteoporosis or those at high risk of bone fractures. Understanding these benefits can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options.
One of the primary benefits of Prolia is its ability to significantly reduce the risk of fractures. Clinical studies have shown that it decreases the likelihood of both vertebral and non-vertebral fractures by inhibiting bone resorption. This is particularly important for postmenopausal women and older adults, who are more susceptible to osteoporosis.
Additionally, Prolia has a well-established safety profile and is administered via a simple subcutaneous injection every six months. This less frequent dosing schedule can enhance patient compliance compared to daily or weekly oral medications. Moreover, patients have reported an improvement in bone mineral density (BMD) as a result of treatment with Prolia, which further supports its effectiveness in managing osteoporosis.
| Benefits of Prolia |
|---|
| Reduces risk of fractures |
| Improves bone mineral density |
| Simple dosing regimen (every 6 months) |
| Well-established safety profile |
Understanding RSV Vaccine
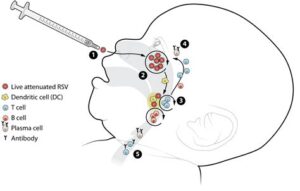
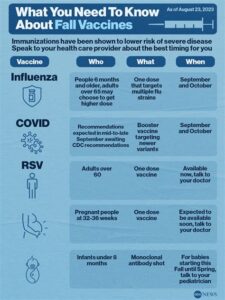
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that leads to severe respiratory infections, especially in infants and older adults. Vaccination against RSV is critical in preventing these infections and their associated complications. The RSV vaccine is designed to stimulate the immune system, enabling it to better combat this virus.
The importance of the RSV vaccine cannot be overstated, particularly for vulnerable populations. Priority groups include premature infants, children with certain health conditions, and older adults. Early clinical trials of the RSV vaccine have shown promising results, suggesting not only safety but also effectiveness in reducing the incidence and severity of RSV-related illnesses.
Overall, the benefits of the RSV vaccine extend beyond personal health; widespread vaccination can help achieve herd immunity, protecting those who are unable to be vaccinated. It is essential to discuss any questions or concerns with a healthcare provider to fully understand the benefits and potential risks associated with the vaccine.
The Importance of RSV Vaccine
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a significant cause of respiratory illness among infants and the elderly. The importance of the RSV vaccine cannot be overstated as it plays a crucial role in preventing severe illness and hospitalizations caused by this virus.
The RSV vaccine creates immunity against the virus, thereby reducing the chances of severe infections. For vulnerable populations, such as premature infants and those with chronic lung or heart conditions, this vaccine can be a life-saving intervention. Organizations like the CDC recommend vaccination as a part of preventive healthcare.
Moreover, the introduction and widespread administration of the RSV vaccine can lessen the overall burden on healthcare systems. With fewer hospitalizations, healthcare resources can be allocated to treat other critical conditions, highlighting the public health significance of the RSV vaccine in broader community health initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Prolia?
Prolia is a medication primarily used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis. It contains denosumab, which helps prevent bone fractures by inhibiting bone resorption.
What is the RSV vaccine?
The RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) vaccine is designed to prevent infections caused by the RSV, a common virus that can lead to severe respiratory illnesses, particularly in infants and older adults. Research is ongoing to develop effective vaccines against RSV.
Is it safe to receive Prolia and the RSV vaccine together?
Generally, there is no known interaction between Prolia and the RSV vaccine. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss individual health conditions and potential risks.
Who should consider getting the RSV vaccine?
The RSV vaccine is especially recommended for infants, young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems who are at a higher risk for severe RSV infections.
How does Prolia work to prevent bone fractures?
Prolia works by inhibiting a protein called RANKL, which is involved in the formation and activity of osteoclasts (the cells that break down bone). By reducing the activity of these cells, Prolia helps maintain or increase bone density, thereby lowering the risk of fractures.
What are the common side effects of Prolia?
Common side effects of Prolia may include back pain, pain in the arms or legs, high cholesterol levels, and urinary tract infections. Serious side effects could also occur, so monitoring by a healthcare provider is important.
What should patients know about the timing of receiving vaccines while on Prolia?
Patients receiving Prolia should discuss their vaccination schedule with their healthcare provider. Timing may depend on individual health status and vaccination guidelines, but generally, vaccines can be administered when indicated.