Explore the COVID-19 vaccine, mRNA technology, its effectiveness, common side effects, and the critical importance of vaccination for global health.In the ongoing battle against infectious diseases, the COVID-19 vaccine has emerged as a crucial tool for safeguarding public health. This blog post delves into the essentials of the COVID-19 vaccine, starting with its fundamental purpose to combat the virus and its variants effectively. We will explore the innovative mRNA technology that underpins most vaccines, offering a glimpse into how this cutting-edge approach works to elicit strong immune responses. Additionally, we’ll examine the vaccine’s effectiveness, common side effects, and the vital importance of getting vaccinated to protect not only ourselves but also our communities. As we navigate through this comprehensive overview, the goal is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about vaccination in a world still grappling with the repercussions of the pandemic.
What is the COVID-19 vaccine?
The COVID-19 vaccine is a medical preparation designed to provide immunity against the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes the disease known as COVID-19. Developed in response to the global pandemic, these vaccines aim to reduce the severity of illness and curb the spread of the virus within communities.
There are several types of COVID-19 vaccines available, including mRNA vaccines, vector-based vaccines, and inactivated or live attenuated vaccines. mRNA vaccines (such as Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) utilize genetic material to instruct cells in the body to produce a harmless piece of the virus, prompting an immune response. On the other hand, vector-based vaccines (like Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen vaccine) use a modified virus to deliver genetic material coding for specific viral proteins.
The introduction of the COVID-19 vaccine has been pivotal in the efforts to control the pandemic. Widespread vaccination aims to establish community immunity, which is critical in protecting those who are most vulnerable and preventing healthcare systems from being overwhelmed. As vaccination rates increase, public health authorities anticipate a significant reduction in COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and deaths.
Understanding the mRNA technology
The advent of the mRNA technology has redefined the landscape of vaccination. Unlike traditional vaccines that use weakened or inactivated forms of a virus, mRNA vaccines teach our cells how to produce a protein that triggers an immune response. This innovative approach not only accelerates the development process but also enhances the effectiveness of vaccines.
At the core of mRNA technology is the messenger RNA (mRNA) itself, which acts as a blueprint for our cells. Once injected, the mRNA enters our cells and utilizes the cellular machinery to create the viral protein. This protein is recognized by the immune system, leading to the production of antibodies, which are critical for fighting off the actual virus in future encounters. The simplicity of this method allows for a quick and adaptable response to emerging pathogens.
Importantly, mRNA does not alter our DNA. After the protein is made, the mRNA is broken down and eliminated by the body. This safe and effective mechanism has played a crucial role in the rapid development of the COVID-19 vaccine, illustrating the transformative potential of mRNA technology in the field of immunization.
Effectiveness of the vaccine
The effectiveness of the vaccine is a crucial factor in its role in controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Vaccines are developed to reduce the severity of illness, prevent hospitalization, and decrease the risk of death. Various studies have shown that the COVID-19 vaccine significantly reduces the chances of contracting the virus and minimizes the risk of developing severe symptoms.
According to several clinical trials and real-world studies, the COVID-19 vaccines have demonstrated high efficacy rates. For instance, mRNA vaccines like those from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna showed an efficacy of approximately 94-95% in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 during the pivotal trials. This effectiveness has been seen across different demographic groups, including various age ranges and ethnic backgrounds.
Moreover, emerging data indicate that the effectiveness can vary based on several factors, such as the circulating variants of the virus and the time since vaccination. Booster doses have been recommended to enhance and prolong immunity, especially in the face of waning protection and the emergence of new variants of concern. As vaccine research continues, ongoing evaluations will help to better understand the long-term effectiveness of the vaccine and the necessity of booster shots.
Common side effects of the vaccine
The COVID-19 vaccine has proven to be a crucial tool in combating the pandemic, but like any medical intervention, it may come with certain side effects. Understanding these side effects helps individuals make informed decisions about their health. Here, we’ll explore the most common side effects associated with the COVID-19 vaccine.
- Pain at the injection site: Many people experience mild to moderate pain, redness, or swelling where the shot was administered.
- Fatigue: A feeling of tiredness is commonly reported, often lasting a day or two after the vaccination.
- Headache: Some individuals may experience headaches, which can vary in intensity.
- Muscle aches: General muscle soreness or aches are frequently reported post-vaccination.
- Fever and chills: A mild fever may develop as the body responds to the vaccine, usually resolving within a day or two.
These side effects are typically mild and resolve on their own. They are a sign that the body is building protection against the virus. It’s important to note that serious side effects are rare, and the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the potential for discomfort.
If you experience side effects that are more severe or last longer than a few days, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Keeping track of your symptoms can help provide valuable information when discussing your experience with a doctor.
In summary, understanding the common side effects of the vaccine can help alleviate fears and encourage more people to get v
Importance of getting vaccinated
Vaccination plays a critical role in protecting public health. It not only helps individuals avoid serious illness but also contributes to the larger goal of herd immunity. When a significant portion of the population is vaccinated, the spread of the virus is significantly reduced, thereby protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical conditions.
The COVID-19 vaccine has demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing hospitalizations and severe cases of the disease. This is crucial for maintaining healthcare capacity, as overwhelmed hospitals can lead to poorer outcomes for all patients, not just those infected with COVID-19.
Furthermore, getting vaccinated can help to prevent variants of the virus from emerging. The more the virus circulates, the higher the chance of mutations, which could make vaccines less effective. By vaccinating a large number of people, we can limit the virus’s ability to mutate and maintain the effectiveness of our current vaccines.
Ultimately, vaccination is not just an individual choice; it’s a community responsibility. By getting vaccinated, individuals help to reduce transmission rates, protect vulnerable populations, and contribute to the eventual containment of the pandemic.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the RSV COVID vaccine?
The RSV COVID vaccine refers to vaccines designed to protect against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in conjunction with COVID-19, focusing on providing immunity to both viral infections.
Why is there a need for an RSV COVID vaccine?
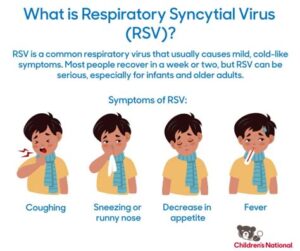
There is a need for an RSV COVID vaccine because both RSV and COVID-19 can cause severe respiratory illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations such as infants, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions.
How does the RSV COVID vaccine work?
The RSV COVID vaccine works by introducing a harmless component of the virus into the body, prompting the immune system to recognize and remember the virus, thus providing protection upon exposure.
Who is eligible for the RSV COVID vaccine?
Eligibility for the RSV COVID vaccine typically includes infants, older adults, and individuals with compromised immune systems, but recommendations may vary based on local health guidelines.
Are there any side effects associated with the RSV COVID vaccine?
Common side effects of the RSV COVID vaccine may include pain at the injection site, mild fever, or fatigue, though serious side effects are rare.
When should individuals get the RSV COVID vaccine?
Individuals should consult their healthcare provider for specific vaccination schedules, but generally, the vaccine is recommended during the RSV season or as advised for COVID-19 boosters.
Can the RSV COVID vaccine be taken with other vaccines?
The RSV COVID vaccine may be administered with other vaccines, but it’s essential to follow healthcare provider recommendations and guidance based on personal health circumstances.