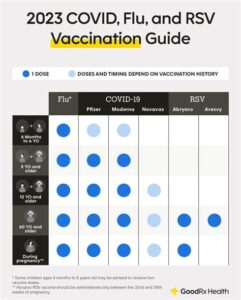
Explore the impact of RSV infection during pregnancy, its risks to the fetus, vaccine safety, clinical trials, and essential recommendations for expectant mothers.As the global health community continues to make strides in vaccination research, the focus on Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) has intensified, particularly concerning its implications during pregnancy. RSV infections can pose significant risks, not only to pregnant women but also to their developing fetuses. Understanding these potential dangers is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare providers alike. With ongoing research into the safety and efficacy of RSV vaccines, many are left wondering how these developments could alter the landscape of maternal and fetal health. This blog post will explore the intersection of RSV infection and pregnancy, outline the associated risks, delve into clinical trials and research findings, and ultimately provide recommendations for pregnant women regarding the RSV vaccine. Join us as we unravel the complexities of RSV vaccination during this critical time.
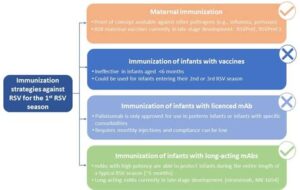
RSV infection and pregnancy
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that can lead to significant respiratory issues, particularly in infants and young children. During pregnancy, the implications of RSV can be of considerable concern for both the mother and the developing fetus. Research indicates that expectant mothers who contract RSV may face increased risks, including complications that could impact their pregnancy.
Pregnant women often experience altered immune responses, which can make them more susceptible to viral infections like RSV. This susceptibility raises questions about maternal health and the potential effects on the fetus. Most notably, RSV infection during pregnancy has been associated with risks such as premature labor and low birth weight.
Moreover, there is ongoing research to understand the long-term effects of RSV exposure during pregnancy. The viral infection may not only affect immediate pregnancy outcomes but could also have implications for the child’s respiratory health later in life. Ensuring that pregnant women are informed about RSV, its risks, and the potential preventive measures,
Potential risks to the fetus
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a significant concern during pregnancy due to its potential to impact both the mother and the developing fetus. Understanding the risks associated with RSV infection during this critical period is essential for the well-being of both parties.
One of the primary concerns is that a pregnant woman infected with RSV can experience complications, which may subsequently affect her fetus.
- Preterm birth: An RSV infection in the mother can lead to complications that may result in a premature delivery.
- Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR): Some studies suggest that RSV can affect the nutritional environment of the fetus, leading to growth issues.
- Low birth weight: Babies born to mothers with RSV may be smaller than expected due to the impact of the infection during pregnancy.
Moreover, if a newborn is infected with RSV shortly after birth, they may experience more severe symptoms, which can lead to hospitalization. Therefore, exploring preventive measures, such as vaccination options, becomes crucial. The implications of RSV can extend beyond the short-term, potentially affecting the developmental milestones of the child.
Safety and efficacy of RSV vaccine
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a significant cause of respiratory illnesses, particularly in infants and young children. With the development of the RSV vaccine, there’s been a growing interest in understanding its safety and efficacy, especially for pregnant women.
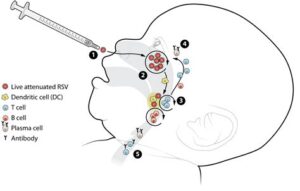
Recent studies have shown that the RSV vaccine can effectively reduce the risk of RSV infection in infants. Clinical trials reported successful results, demonstrating that the vaccine induced a robust immune response in mothers, which subsequently provided protective antibodies to their newborns. This transference of immunity is crucial in the fight against RSV, as newborns are particularly vulnerable.
In terms of safety, preliminary data indicates that the RSV vaccine does not pose significant risks to expectant mothers or their babies. Most participants in clinical trials experienced minimal side effects, which were mild and temporary, such as soreness at the injection site or low-grade fever. It’s reassuring to note that larger studies continue to monitor the long-term effects of the vaccine on both mothers and their infants.
Clinical trials and research findings
In recent years, extensive research has been conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the RSV vaccine during pregnancy. Clinical trials have provided valuable insights into how the vaccine affects both mothers and fetuses. One significant study focused on the administration of the RSV vaccine to pregnant women in their third trimester, aiming to understand its impact on the newborn’s immune response.
Results from these clinical trials have shown promising outcomes. In one trial involving over 3,000 pregnant women, the data indicated that the RSV vaccine not only elicited a robust immune response in the mothers but also transferred protective antibodies to the infants. This transference is crucial for protecting newborns from RSV during their early months when they are most vulnerable.
Moreover, the trials reported minimal adverse effects among the participants, supporting the notion that the RSV vaccine is a safe option during pregnancy. As research continues, these findings are contributing to increased confidence among healthcare providers and expectant mothers regarding the use of the RSV vaccine as a preventative measure against RSV infection.
Recommendations for pregnant women
When considering the RSV vaccine during pregnancy, it’s essential for pregnant women to stay informed about their options and consult health care professionals for personalized advice. The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) can pose serious risks, particularly to newborns, making vaccination decisions critical.
- Consult Your Health Care Provider: Always discuss with your doctor whether the RSV vaccine is suitable for you during your pregnancy.
- Stay Updated on Vaccination Guidelines: Follow the latest health guidelines and recommendations from organizations like the CDC and WHO regarding RSV vaccination.
- Consider Timing: The timing of the vaccine might impact its efficacy. Ensure you discuss the best time during your pregnancy to receive the vaccine if recommended.
Additionally, it’s vital for pregnant women to be aware of any potential side effects associated with the vaccine and to report any unusual symptoms to their health care provider. Understanding the risks and benefits of vaccination can help in making an informed decision that is best for both the mother and the baby.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RSV and why is it a concern during pregnancy?
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that can cause serious respiratory infections, particularly in young children. During pregnancy, it is important to understand RSV as it can affect newborns who are at higher risk for severe illness.
How does the RSV vaccine work?
The RSV vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that protect against RSV infection. It is designed to be given to pregnant individuals to help pass immunity to their babies.
Is the RSV vaccine safe for pregnant individuals?
Current studies indicate that the RSV vaccine is safe for pregnant individuals. However, it is always essential to consult a healthcare provider to discuss any potential risks.
When should the RSV vaccine be administered during pregnancy?
The RSV vaccine is typically recommended during the later stage of pregnancy, usually between weeks 24 to 36, to ensure that the baby receives adequate antibodies before birth.
What are the benefits of getting the RSV vaccine during pregnancy?
The primary benefit is the protection it offers newborns against severe RSV infections. Maternal vaccination can result in transferred immunity, helping reduce the risk of hospitalization in newborns.
Are there any side effects of the RSV vaccine during pregnancy?
While side effects can vary, most individuals experience mild effects like soreness at the injection site, fatigue, or mild fever. Serious side effects are rare, but it’s important to monitor any unusual symptoms.
Can breastfeeding individuals receive the RSV vaccine?
Yes, breastfeeding individuals can receive the RSV vaccine. The antibodies produced may continue to provide protective benefits to the infant through breast milk.