Explore the RSV vaccine‘s development, effectiveness, side effects, and expert recommendations to safeguard against respiratory syncytial virus in vulnerable populations.As respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) continues to pose significant health risks, particularly for infants and the elderly, the development of an RSV vaccine has emerged as a critical focus in modern medicine. With organizations like the Mayo Clinic at the forefront of research and innovation, the quest to combat this viral infection is gaining momentum. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the essential aspects of the RSV vaccine—from its underlying science to the extensive research that has shaped its development. We’ll also explore its effectiveness, potential side effects, and the latest recommendations for those who may benefit from this groundbreaking vaccine. By unraveling these components, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how the RSV vaccine can protect vulnerable populations and contribute to improved public health outcomes.
Understanding the RSV Vaccine
The RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) vaccine is a critical advancement in public health aimed at preventing respiratory infections, particularly in vulnerable populations such as infants and older adults. RSV is a common virus that can lead to serious respiratory illness and is known to be a significant cause of hospitalizations among young children. Understanding the RSV vaccine is essential for both healthcare professionals and the general public to minimize the impact of this virus.
Recent developments in *vaccine technology* have paved the way for the creation of the RSV vaccine. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to recognize and combat the virus effectively. This innovation is particularly vital since RSV can be quite severe, especially for premature infants and those with underlying health conditions. There are currently several candidates undergoing clinical trials, which are likely to lead to widespread usage in the near future.
One of the most significant benefits of the RSV vaccine is its ability to drastically reduce RSV-related hospitalizations and complications. As recommended by major health organizations, receiving the RSV vaccine not only protects individual children but also contributes to herd immunity, safeguarding those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical constraints. Understanding the importance and functioning
Development of the RSV Vaccine
The development of the RSV vaccine has been a long and complex journey, reflecting the challenges associated with creating vaccines for respiratory viruses. Initially, research on Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) began in the 1960s, sparking interest due to the severe respiratory illness it causes, particularly in infants and older adults.
Early attempts to create a vaccine were met with significant setbacks. A formalin-inactivated RSV vaccine candidate was tested in children but resulted in enhanced disease upon natural infection, leading to severe adverse effects. This outcome highlighted the need for a more refined approach in developing a safe and effective vaccine.
Despite these challenges, recent advancements in technology and a better understanding of the virus’s structure have reinvigorated efforts to create an effective RSV vaccine. Currently, various vaccine candidates are under investigation, utilizing innovative platforms such as mRNA technology, live attenuated viruses, and viral vector systems. Researchers aim to achieve robust immunity while minimizing side effects, reflecting a hopeful pathway toward availability.
Effectiveness of the RSV Vaccine
The effectiveness of the RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) vaccine is a critical aspect to evaluate as it directly impacts public health outcomes. Recent clinical studies have shown promising results, indicating that the vaccine significantly reduces the incidence of RSV infections in both infants and at-risk adult populations.
In a recent trial conducted by the Mayo Clinic, researchers found that the RSV vaccine demonstrated an efficacy rate of approximately 85% in preventing severe respiratory illness caused by the virus in infants. The vaccine works by stimulating the body’s immune system to produce antibodies that specifically target RSV, thus providing a robust defense against infections.
Furthermore, ongoing studies continue to confirm that the immune response generated by the RSV vaccine not only protects against the virus but also minimizes the risk of complications, such as hospitalizations and long-term pulmonary issues. This effectiveness highlights the vaccine’s potential to become a standard preventative measure for vulnerable populations.
| Group | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|
| Infants | 85% |
| Children with underlying conditions | 78% |
| Adults over 65 | 72% |
Side Effects of the RSV Vaccine
The RSV vaccine has been developed to protect individuals, particularly infants and elderly adults, from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. However, like any medical intervention, it is crucial to consider the side effects that may accompany the vaccine.
- Pain at the injection site
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fever
Most side effects are typically mild and resolve within a few days. However, monitoring for any serious side effects is essential, as some individuals may experience more pronounced reactions. It is important to rep
Recommendations for the RSV Vaccine
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common virus that can lead to serious respiratory illness, particularly in infants and older adults. The RSV vaccine offers a promising way to help prevent these outcomes. The Mayo Clinic and health organizations around the world provide guidelines regarding the appropriate use and recommendations for the RSV vaccine.
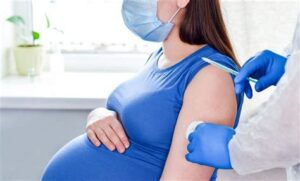
According to the Mayo Clinic, the primary recommendation for the RSV vaccine is aimed at high-risk populations. This includes infants born prematurely, children with chronic lung disease, or those with weakened immune systems. Vaccination is suggested for these cohorts to help reduce the incidence of severe RSV-related complications. Furthermore, pregnant women are encouraged to receive the vaccine in the later stages of pregnancy, as it can provide protective antibodies to their newborns.
For the general population, the Mayo Clinic notes that the RSV vaccine is still under evaluation, and recommendations may evolve as more data becomes available. It’s essential for individuals to stay informed and consult healthcare professionals regarding the suitability of the vaccine based on personal health circumstances.
In summary, the Mayo Clinic emphasizes the importance of targeting high-risk groups while continuing research and evaluations for the broader population. Staying updated with the latest recommendations ensures better protection against RSV.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RSV and why is it significant?
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus that can cause severe respiratory infections, especially in infants and older adults. It is significant because it leads to hospitalizations and can be life-threatening for vulnerable populations.
What is the purpose of the RSV vaccine being developed at Mayo Clinic?
The RSV vaccine being developed at Mayo Clinic aims to provide immunity against RSV, reducing the risk of severe infections and hospitalizations, particularly in high-risk groups like infants and the elderly.
Who is the target population for the RSV vaccine?
The primary target population for the RSV vaccine includes infants, young children, and older adults, who are most at risk for severe RSV-related complications.
What progress has been made in RSV vaccine research at the Mayo Clinic?
Mayo Clinic researchers have made significant strides in developing and testing RSV vaccines, including conducting clinical trials to evaluate their safety and effectiveness.
How does the RSV vaccine work?
The RSV vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight the virus, thereby providing protection against future infections.
What are the potential benefits of an RSV vaccine?
Potential benefits of an RSV vaccine include reducing the incidence of severe RSV infections, lowering hospitalization rates, and ultimately decreasing healthcare costs associated with treating RSV-related illnesses.
When is the RSV vaccine expected to be available to the public?
While timelines may vary, the availability of the RSV vaccine to the public will depend on the completion of clinical trials and regulatory approvals; updates should be monitored through health authorities and Mayo Clinic announcements.