Explore the significance of RSV infections in adults, the importance and benefits of vaccination, current recommendations, and future trends in RSV vaccination.As respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) continues to emerge as a significant health concern in adults, understanding and addressing its impact is more crucial than ever. Traditionally associated with infants, RSV can also cause severe respiratory illness in older adults and those with underlying health conditions. This blog post delves into the complexities of adult RSV infections, emphasizing the importance of vaccination as a preventive measure. We will explore current recommendations regarding RSV vaccines for adults, highlighting the myriad benefits these vaccinations offer to various adult populations. Additionally, we’ll look ahead to future trends in RSV vaccination, ensuring you stay informed on this vital aspect of adult health. Whether you’re a healthcare provider or simply seeking knowledge for yourself or loved ones, this guide will equip you with essential insights into RSV and the safeguards available against it.
Understanding Adult RSV Infections
Respiratory Syncytial Virus, commonly known as RSV, is often associated with severe respiratory infections in infants and young children, but it can also significantly impact adults. In fact, RSV infections in adults are increasingly recognized as an important public health concern, especially among the elderly and those with underlying health conditions.
Symptoms of RSV in adults can range from mild cold-like signs to more severe respiratory issues. Common symptoms include coughing, sneezing, sore throat, and difficulty breathing. While many adults may recover without medical intervention, those who are older or have compromised immunity can experience serious complications such as pneumonia, which may require hospitalization.
Understanding the impact of RSV in the adult population is critical, as it can lead to increased morbidity and mortality. The recognition of RSV as a significant health threat in adults emphasizes the need for effective vaccination strategies to reduce the burden of this virus, particularly in vulnerable groups. As we advance our understanding of adult RSV infections, ongoing research and public health initiatives will be pivotal in addressing this concern.
Importance of RSV Vaccines for Adults
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) has long been associated with severe respiratory illnesses in infants and young children, but its impact on adults is equally concerning. In fact, RSV infections can lead to significant morbidity and mortality among older adults and those with underlying health conditions. Understanding the importance of RSV vaccines for adults is therefore crucial in preventing outbreaks and safeguarding vulnerable populations.
Vaccination can play a pivotal role in reducing the incidence of RSV-related hospitalizations and complications. Older adults, particularly those over the age of 65, are at a higher risk of severe RSV infections, making the need for effective vaccines more pressing. These vaccines can help not only protect individuals from getting infected but also mitigate the overall burden on healthcare systems, especially during peak RSV seasons.
Moreover, vaccine development for RSV has been progressing significantly in recent years. With promising results from clinical trials, there is optimism about the introduction of RSV vaccines that are specifically tailored for adult populations. These advancements highlight the critical need for awareness and support for RSV vaccination programs targeted at adults, ensuring that those most at risk are adequately protected.
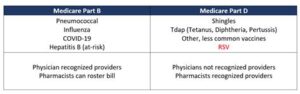
Current RSV Vaccine Recommendations for Adults
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) has traditionally been recognized as a major cause of respiratory illness in infants and young children, but it can also significantly impact adults, particularly those with underlying health conditions. Recognizing the growing importance of RSV in adult populations, health organizations have established various vaccine recommendations to prevent severe infections.
The CDC and other public health authorities recommend RSV vaccination especially for specific groups of adults. These include individuals aged 65 years and older, as well as adults aged 18 years and older who have chronic heart or lung diseases, weakened immune systems, or other significant health issues. Vaccination is encouraged during the RSV season, which typically runs from late fall to early spring.
Currently, several vaccines are in various stages of development and approval for RSV. Some have shown promising results in clinical trials, leading to expectations that we will soon see routine immunizations for RSV in adults.
| Group | Vaccine Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Adults 65 and older | Recommended to receive the RSV vaccine before the onset of the RSV season. |
| Adults with chronic conditions | Advised to get vaccinated to prevent severe RSV infections, especially during the RSV season. |
| General adult population | Vaccination may be recommended based on emerging evidence and vaccine approvals. |
As the medical community continues to gather data regarding the efficacy and safety of RSV vaccinations for adults, recommendations may evolve. It’s crucial for adults at higher risk to consult with healthcare providers r
Benefits of RSV Vaccination in Adult Populations
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is commonly known for its impacts on children, but adults are not immune from its potential dangers. In recent years, growing evidence underscores the importance of RSV vaccination for adult populations, particularly vulnerable groups. Understanding the benefits of vaccination is crucial for promoting better health outcomes and preventing serious complications related to RSV infections.
One of the key benefits of RSV vaccination for adults is the significant reduction in hospitalizations. Studies have shown that vaccination can lower the incidence of RSV-related hospital visits by as much as 80%. This is especially critical for older adults and those with underlying health conditions, who are at higher risk of severe illness from RSV. By receiving the vaccine, they effectively shield themselves from potentially life-threatening complications.
Additionally, widespread vaccination in adult populations can contribute to herd immunity, reducing the overall circulation of the virus in the community. This not only protects individuals but also provides a layer of safety for vulnerable populations, such as infants and the elderly. By preventing RSV transmission, the benefits of vaccination can have a far-reaching impact on public health.