Explore the importance of pneumonia vaccines, the impact of RSV on respiratory health, and essential preventive measures for both conditions.In the realm of respiratory health, two significant concerns are the pneumonia vaccine and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). As we delve deeper into these topics, it’s essential to understand what each vaccine offers and how they can contribute to public health. The pneumonia vaccine plays a crucial role in preventing infections that can lead to severe complications, while RSV is a common virus that can pose serious health risks, particularly to infants and the elderly. This blog post aims to shed light on the significance of the pneumonia vaccine, the impact of RSV on respiratory health, and the necessary preventive measures for both conditions. By equipping ourselves with knowledge about these vaccines, we can better navigate the landscape of respiratory illnesses and safeguard our health and the health of our loved ones.
Understanding Pneumonia Vaccine
The pneumonia vaccine is vital in protecting against various strains of pneumonia, particularly those caused by the bacteria *Streptococcus pneumoniae*. Vaccination reduces the risk of pneumonia and other serious infections for at-risk populations, including the elderly and those with compromised immune systems.
There are generally two types of pneumonia vaccines available: the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) and the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13). The PPSV23 vaccine protects against 23 different serotypes of *S. pneumoniae*, while the PCV13 vaccine covers 13 serotypes and helps prevent infections in young children. Understanding these vaccines is essential for informed decision-making regarding vaccination schedules.
It’s important to note that while the pneumonia vaccine is effective, it does not cover all types of pneumonia—for example, viral pneumonia, which can be caused by influenza or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Therefore, it is part of a comprehensive approach to respiratory health, often combined with other preventive measures and vaccines.
RSV: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a significant viral pathogen that primarily affects the respiratory system. It’s particularly notorious for causing respiratory infections in infants and young children. RSV can lead to bronchiolitis and pneumonia, conditions that may require medical attention. Understanding RSV is crucial, especially for parents and caregivers of young children who are at a heightened risk of severe illness.
Transmission of RSV occurs through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also survive on surfaces, making it easy for the virus to spread in crowded settings. As a result, RSV is a common cause of hospitalizations during the winter months when the virus circulates more widely.
The symptoms of RSV infection can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include coughing, runny nose, and fever, which can develop into more serious complications such as wheezing and difficulty breathing. For many, RSV is a common cold, but in high-risk groups, including premature infants and those with underlying health conditions, it can lead to serious respiratory diseases.
Preventive measures for RSV include maintaining good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, and minimizing contact with infected individuals. In some cases, a preventive medication may be recommended for high-risk infants to help reduce the severity of the disease. Understanding how to recognize and respond to RSV is vital in protecting vulnerable populations.
Significance of Pneumonia Vaccine
The pneumonia vaccine plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals against infections that can lead to serious respiratory illnesses. This vaccine is designed to protect against specific types of bacteria that cause pneumonia, primarily Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is responsible for a significant portion of pneumonia cases worldwide.
Vaccination against pneumonia is particularly significant for vulnerable populations, including the elderly, young children, and those with underlying health conditions. By receiving the vaccine, these groups can significantly reduce their risk of developing pneumonia, which can result in hospitalization or even mortality. Health authorities often recommend the pneumococcal vaccine for these at-risk groups as a preventive measure.
Additionally, the broader importance of the pneumonia vaccine is reflected in its ability to decrease the overall burden on healthcare systems. Fewer cases of severe pneumonia contribute to reduced healthcare costs and lessen the strain on medical resources. Public health campaigns promoting vaccination are fundamental in achieving higher coverage rates, thereby enhancing community immunity against this potentially deadly disease.
Impact of RSV on Respiratory Health
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a significant cause of respiratory illnesses, especially in infants and young children. This virus can lead to a range of respiratory issues, from mild cold-like symptoms to more severe conditions such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia. According to recent studies, RSV is responsible for a considerable number of hospitalizations in children under the age of five, highlighting its widespread impact on respiratory health.
The prevalence of RSV brings attention to the importance of understanding its effects. For example, infants are particularly vulnerable to the virus as their respiratory systems are still developing. In some cases, RSV can lead to long-term respiratory complications, including asthma and other chronic lung diseases, which can affect a child’s health well into adulthood.
Furthermore, RSV poses a risk not only to young children but also to elderly individuals and those with weakened immune systems. In senior adults, RSV can exacerbate existing health issues, leading to increased morbidity and mortality rates. Thus, the impact of RSV on respiratory health is profound, necessitating preventive measures, awareness, and ongoing research into effective treatments and vaccines.
Preventive Measures for RSV and Pneumonia
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and pneumonia are significant health concerns, especially for infants, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune systems. Effective preventive measures can help mitigate the risks associated with these conditions. Understanding these preventive strategies is crucial for protecting vulnerable populations.
One of the primary ways to prevent the spread of both RSV and pneumonia is through vaccination. The pneumonia vaccine offers protection against pneumonia caused by certain bacteria. In contrast, there is currently no specific vaccine for RSV, but preventive measures can still help reduce its spread.
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Frequent hand washing with soap and water helps eliminate germs that can cause RSV and pneumonia. |
| Avoid Close Contact | Limiting close contact with sick individuals can prevent the spread of respiratory infections. |
| Healthy Environment | Keeping living spaces well-ventilated and free of cigarette smoke minimizes respiratory risks. |
| Vaccination | Receiving pneumonia vaccines like the pneumococcal vaccine can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia. |
| Breastfeeding | For infants, breastfeeding can enhance immunity and lower the likelihood of severe respiratory infections. |
In addition to the measures listed above, educating parents and caregivers about the signs and symptoms of RSV and pneumonia is vital. Early recognition can lead to prompt treatment, which can mitigate severe outcomes. It is also essential for caretakers of children and elderly individuals to stay vigilant and seek medical advice when symptoms arise.
Ultimately, a comprehensive approach to preventive measures for RSV and pneumonia can contribute to better respiratory health outcomes across all age groups. Incorporating these strategies into daily activities helps create a healthier community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are RSV and pneumonia?
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) and pneumonia are both respiratory infections. RSV is a common virus that leads to conditions like bronchiolitis and pneumonia, particularly in infants and young children. Pneumonia, on the other hand, is an infection that inflates the air sacs in one or both lungs, which can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
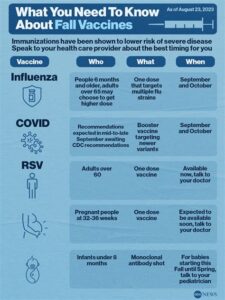
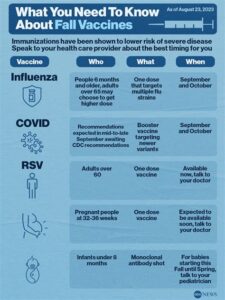
Who should get the RSV vaccine?
The RSV vaccine is primarily recommended for infants and young children, especially those at high risk of severe RSV disease, such as preterm infants or those with underlying health conditions. Vaccination recommendations may vary based on the latest guidelines from health authorities.
Who should receive the pneumonia vaccine?
The pneumonia vaccine is recommended for children under age 2, adults aged 65 and older, and individuals aged 2 to 64 with certain medical conditions, such as chronic lung disease, heart disease, or weakened immune systems.
What are the different types of pneumonia vaccines?
There are two main types of pneumonia vaccines: the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13, PCV15, and PCV20), which protects against 13 to 20 strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae; and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23), which protects against 23 strains.
What are the main benefits of the RSV vaccine?
The RSV vaccine can significantly reduce the risk of severe RSV infection, hospitalizations, and serious complications, particularly in vulnerable populations such as premature infants and those with chronic health conditions.
Can RSV vaccinations prevent pneumonia?
While the RSV vaccine primarily targets RSV, preventing RSV infections can subsequently reduce the risk of pneumonia associated with the virus. However, the pneumonia vaccine directly targets pneumococcal bacteria that can cause pneumonia.
Are there any side effects associated with these vaccines?
Common side effects for both the RSV and pneumonia vaccines may include mild pain at the injection site, fever, fatigue, and irritability. Severe reactions are rare, but individuals should consult with their healthcare provider for detailed information about vaccine safety.